
Route, and will be sending traffic destined to 10/8 via R6.
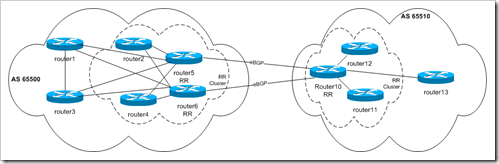
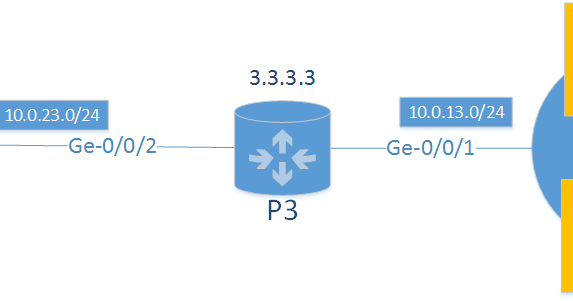
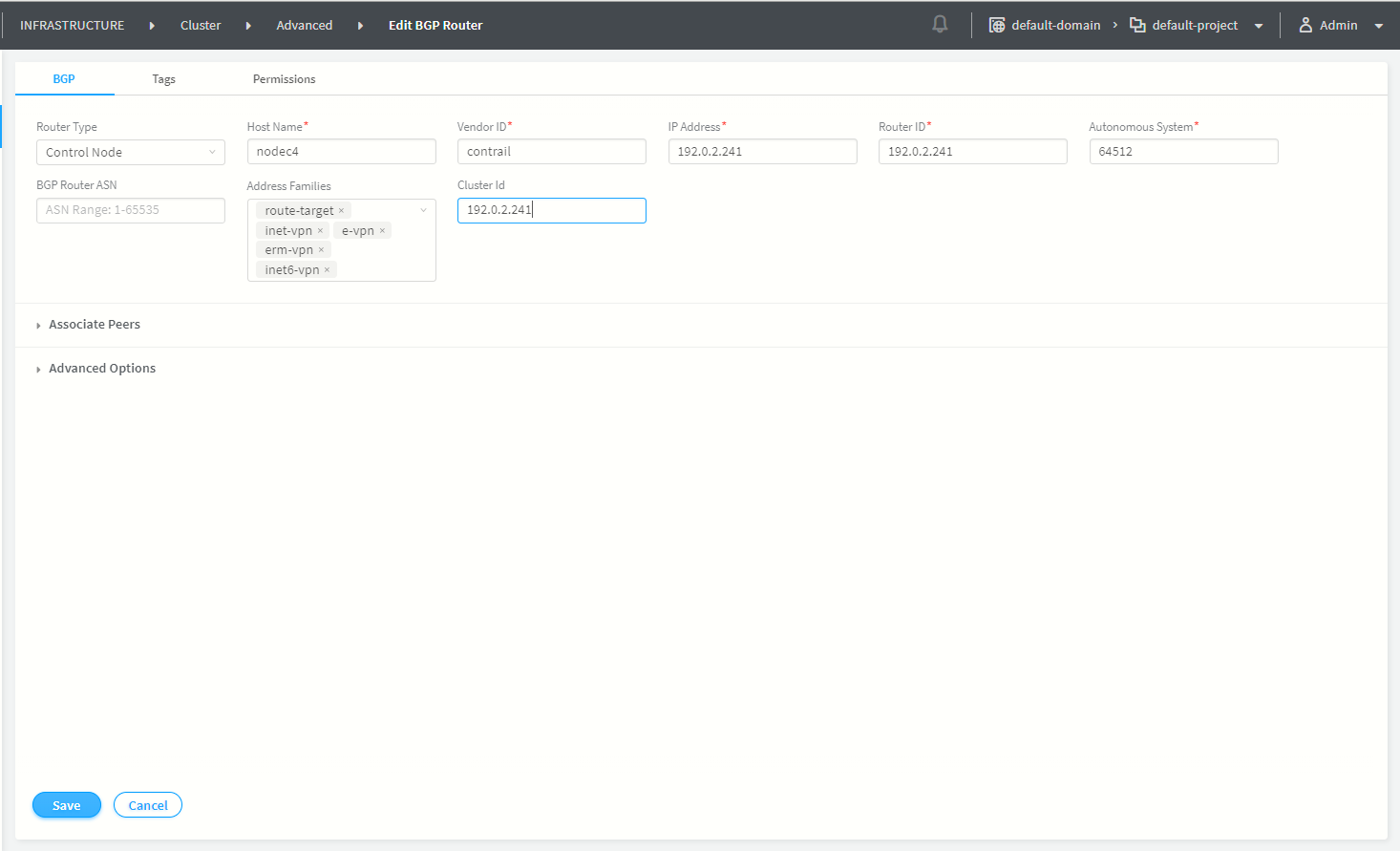
Near R4, and you can see that the IGP metric to get to R4 is much lower thanīecause RR is now selecting R6 as the best route, R7 will only receive this The new router (R7) is physically located This sounds great! But: what if we add another router to this picture? This route is then sent to R5, which now sends traffic destined to 10/8 via R6 (instead of R4). As a result, when RR compares the two routes, the route from R6 is selected (Highest Local Preference). R6 is now advertising the route with a local preference of 300. You might consider using local preference to solve this problem as shown: I know, maybe you can just make that interface 10G as well, but what if you cannot do that, or you cannot do that quickly enough, or you just don’t want to!!!?!? This would not be a source of concern, until you realize that the link between R5 and R4 is 1Gbps, the link between R5 and R6 is 10Gbps, and the 1Gbps link towards R4 is experiencing congestion, delay, and unhappy customers! As a result, R5 only has one route to send traffic to 10/8, using R4 as the next hop.The RR then advertises the route that it selected for itself, to R5.In this example, we are assuming that we are not changing any attributes for the routes other than then next-hop, before R4 and R6 advertise the route to RR, thus RR is choosing the route via R4, based on the router-ids of R4 and R6 (lowest RID). The RR goes through the BGP decision process itself, and choses the route from R4 as the best route.R4 and R6 advertise the route to their route reflector (RR).The route is advertised towards AS400 and accepted by R4 and R6.AS 100 is advertising a route for 10/8 to both R2 and R3 over AS200 and AS300.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
